Once again, Dr. Ted Bunn, UR Department of Physics, nominated our word. This time he picked one that was completely new to me. As Dr. Bunn put it in an e-mail:
Once again, Dr. Ted Bunn, UR Department of Physics, nominated our word. This time he picked one that was completely new to me. As Dr. Bunn put it in an e-mail:
It can just mean gloomy, apparently, but it can also mean “the formal clothing worn for examinations and formal occasions at some universities.” In Dorothy Sayers’s novel set at Oxford, she uses it to describe clothing in dark, subdued shades, suitable for wearing under academic regalia. I always think of it on graduation day.
Only one of my American dictionaries has a brief entry, supporting Professor Bunn’s conclusion that the word is British English, not its American cousin. The OED Online provides both senses of the word given above, as an adjective or noun. The Latin roots are plain, sub + fuscus (dusky). We have a similar derivation in obfuscate and obfuscation.
As recently at 2006, the Times of London noted that “Undergraduates at Oxford University have voted by four to one to retain subfusc costume when sitting examinations.” They voted again to retain it in 2015. There are other specificities for subfusc at Oxford. As I learned from this article about the differences between it and Cambridge, subfusc means “a kind of uniform of a black suit, white shirt and black robe, plus a black tie for men and a black ribbon for women.”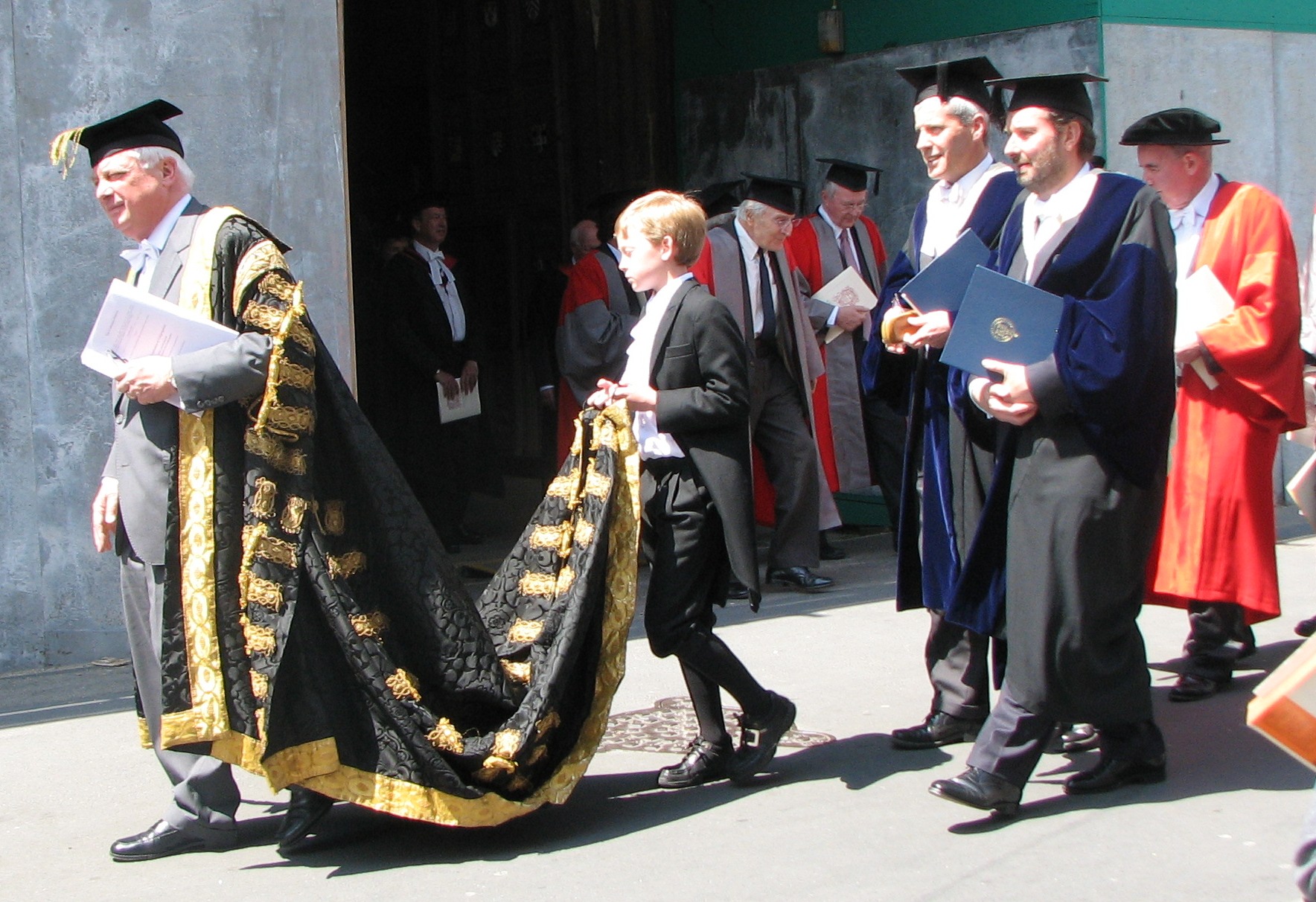
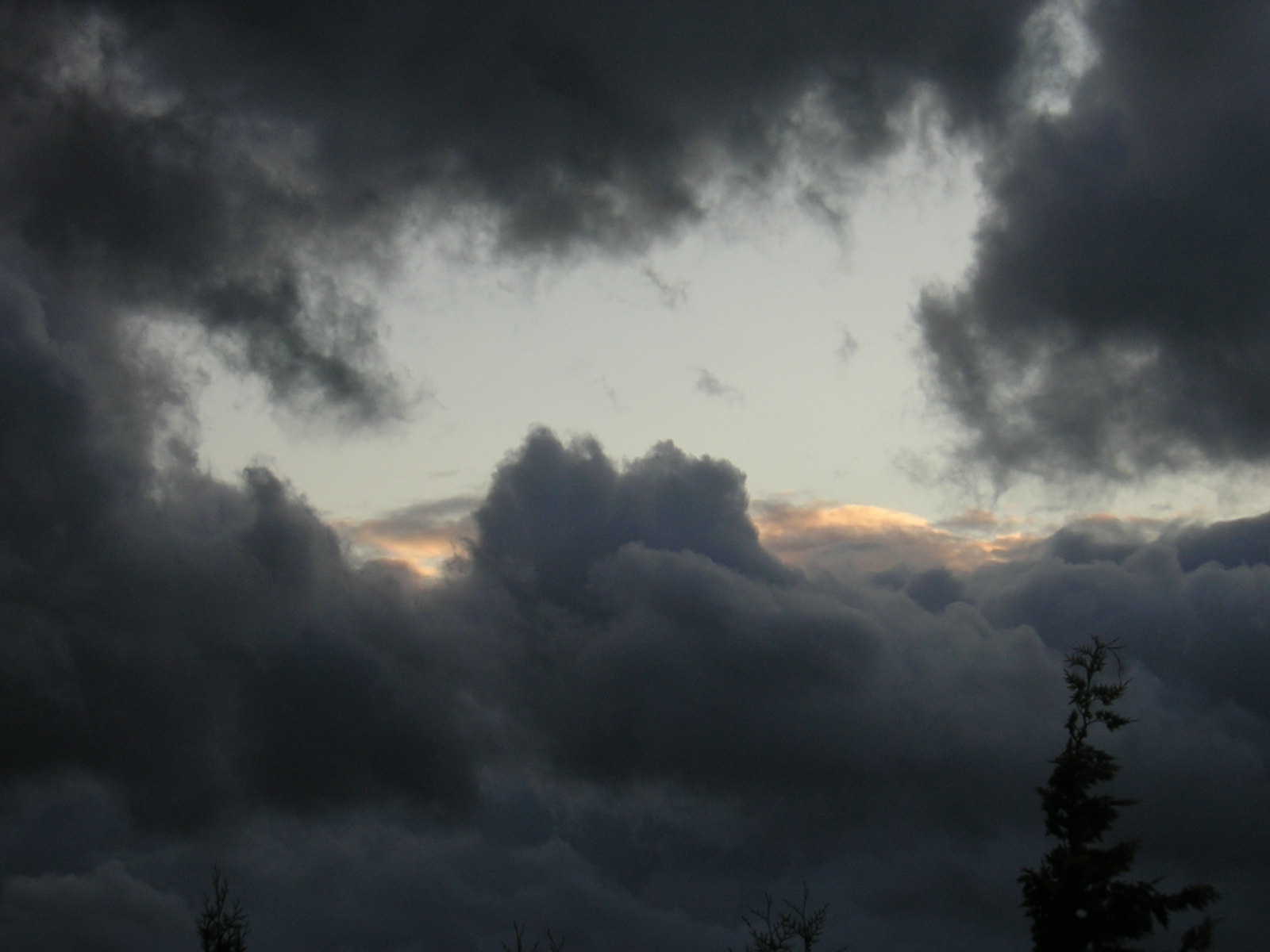
The customs surrounded academic regalia have crossed the Atlantic far better than the word itself or, for that matter, the often subfusc weather of the British Isles. While I cannot find meteorological examples of the word, it certainly works in that context.
The image of a subfusc sky with the light just returning is my own, taken at twilight in Kenmare, Ireland in 2011. The academic regalia of Oxford comes to us courtesy of Wikipedia.
This blog will continue all summer, so nominate a word by e-mailing me (jessid -at- richmond -dot- edu) or leaving a comment below.
See all of our Words of the Week here.