Background
In CHEM 206, you will learn a variety of different reactions. Many of these qualify as condensation reactions, in which two (or more) small molecules (i.e., “monomers”) combine to form a larger molecule. In the process, a small molecule (usually water) is expelled (Figure 1).
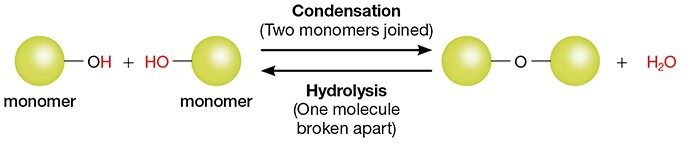
Figure 1. A generic condensation reaction.
In this project, you will use the structure determination skills you learned this semester to determine the outcome of a condensation reaction between vanillin and benzocaine in the presence of acetic acid (Figure 2).
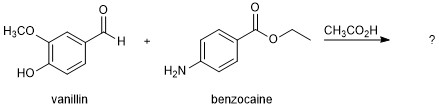
Figure 2. Project 5B reaction puzzle.
Procedure
1. In a 150 mL beaker, combine 1.50 g vanillin and 1.70 g benzocaine.
2. Add 0.5 mL glacial acetic acid to the mixture. You may measure this quantity using the markings on the plastic pipettes available in the lab.
3. Use a microspatula to vigorously mix the components until you obtain a dry yellow powder (~5 minutes).
4. Transfer the solid product to a 125 mL Erlenmeyer flask.
5. Recrystallize the solid using a 9:1 isopropanol:hexane solvent mixture.
6. Collect the recrystallized solid by vacuum filtration.
7. Perform a second recrystallization to further purify the solid. Collect the product by vacuum filtration and allow it to dry on the funnel for at least 30 minutes.
8. Determine the product yield and characterize it by melting point analysis, GC-MS, IR, and NMR.
