Identify is a monthly series here on the SAL blog, focusing on students, faculty, and alumni of University of Richmond who have used GIS in exciting ways. Come by each month to learn more about the interdisciplinary nature of GIS here at UR.
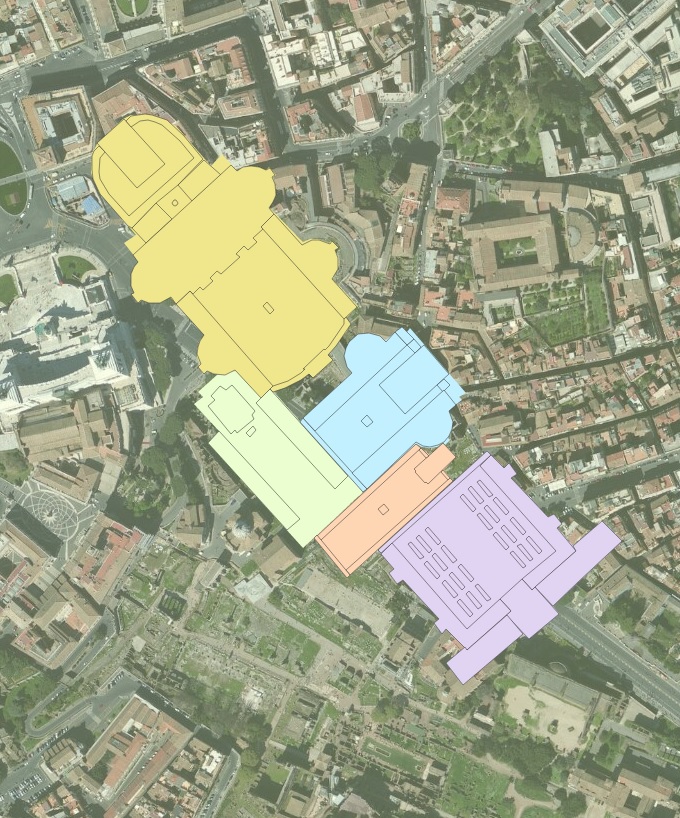
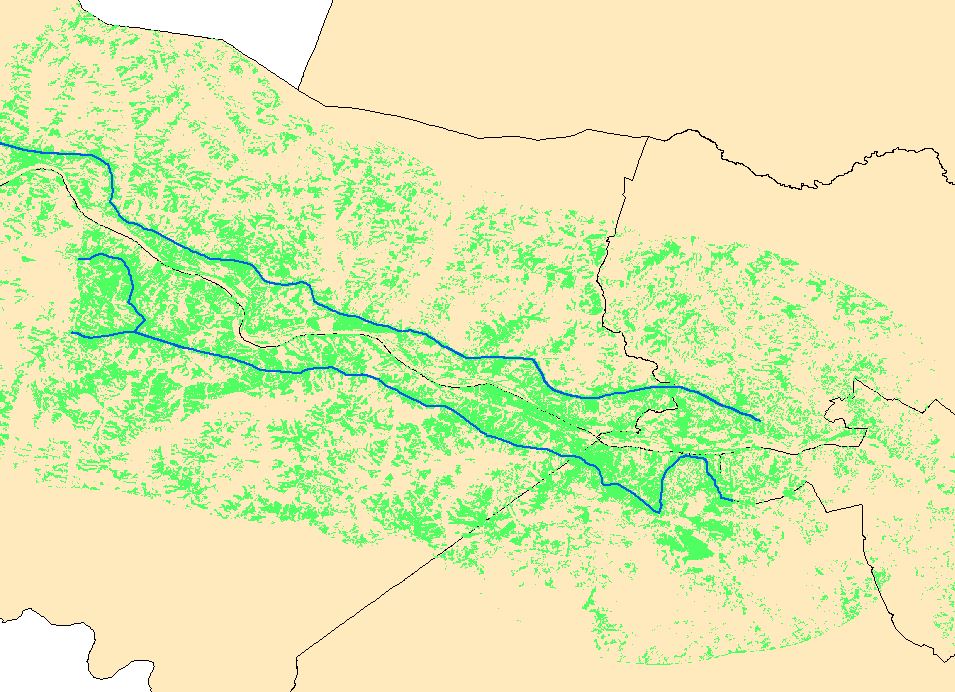
An example of GIS in archaeology: the imperial fora of Rome. Click the image to access an interactive web map!
In the SAL, we like to emphasize how knowledge of GIS can benefit virtually every academic field. Having skill in GIS isn’t “only” for geography or environmental science; it can be applied to a wide range of other natural, physical, and social sciences too. One great example of this cross-disciplinary application of GIS is our partnership with Associate Professor of Classics and Archaeology Dr. Elizabeth Baughan. GIS, of course, is a perfect way to document the results of archaeological digs, and Dr. Baughan has thus made use of GIS both in class and in the field.
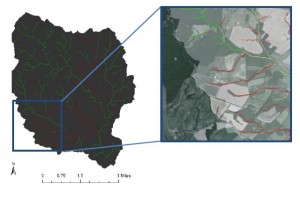
Dr. Baughan frequently brings her Introduction to Archaeology course to the SAL, to familiarize her students with GIS and to show them its power in displaying archaeological data. This class day is “usually a highlight of the semester,” she says, “and it is always interesting to see how many of [the students] have been [to the SAL] for other, very different classes. GIS helps students see unexpected connections across disciplines.” For those students who haven’t yet taken a formal GIS class, many decide to enroll and consequently apply their GIS skills to their own archaeological research. A great example of this process involves this map produced by Samantha Frandsen ’13, a student of Dr. Baughan, showing the locations of the imperial fora of Ancient Rome. You can read more about Frandsen’s work at this link.
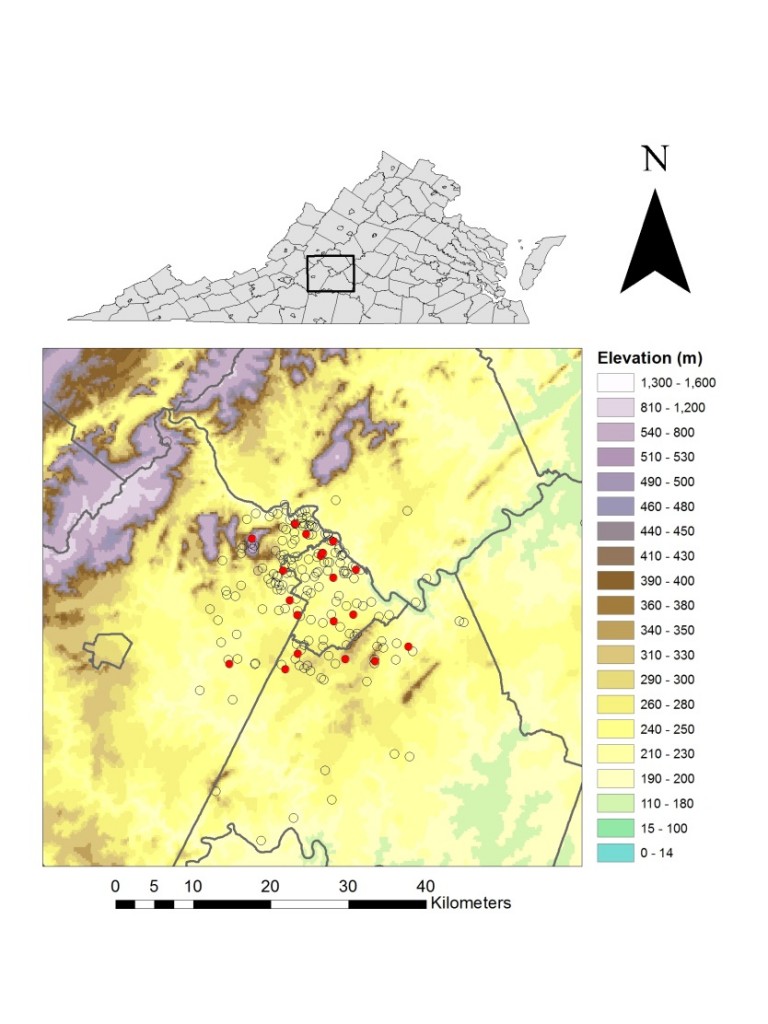
Dr. Baughan also uses GIS while performing archaeological surveys. In particular, Dr. Baughan conducts research in Turkey; she and her colleagues meticulously document their finds and add those data to a GIS for future analysis. For archaeology, she says, GIS has “a wide range of uses and benefits, from the correlation of survey find locations with topographic data and subsurface features …, to understanding regional site distribution in the context of environmental conditions.”
But recently, Dr. Baughan ran into an issue: while the data collected for a recent project would show up in our ArcGIS software, its location would not appear correctly relative to other features on the ground—something was wrong with the data. Dr. Baughan came to the SAL and asked for our assistance; after looking at the data, we discovered an amusing, coincidental reason for the error.
As a necessary first step when working with GIS, a map projection had already been assigned to the data. A projection is a way to transform the spherical surface of the Earth into a flat, two-dimensional plane. In particular, the data had correctly been given a UTM projection for zone 35S, the zone describing the western part of Turkey in which lies one of the survey sites. Nonetheless, the data would not show up.
We noticed, however, that ArcGIS uses a slightly different naming structure for its UTM zones. Rather than adopting the Military Grid Reference System format of using the letters C through X to describe latitudes of north and south in a UTM grid, ArcGIS only uses longitudinal bands, splitting the UTM zones latitudinally just once at the equator. This method results in merely a northern and a southern zone, respectively labeled N and S, for each zone number. Thus, west Turkey rests in zone 35N in ArcMap—zone 35S is in the southern hemisphere instead!
Once we fixed this error, the data aligned well. Dr. Baughan will now be able to perform analyses on the data and further develop her academic research. The SAL was glad to help Dr. Baughan “repair” the data—we know that GIS can be confusing, even for people with experience with the tool, and that often the best results come from team efforts. We look forward to seeing how she will use GIS to analyze the data and to helping her work with any geospatial information she collects on future digs!
Bonus! Listen to Dr. Baughan discuss her research as well as her new book, Couched in Death: Klinai and Identity in Anatolia and Beyond, in the most recent Podcast@Boatwright.